Todd Mitchell
GEOG-499c
|
Lab 4: Raster
Modeling |
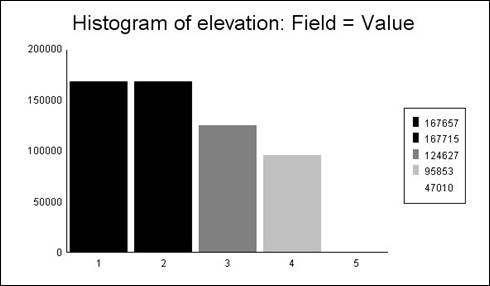
Hand-In 1 (elevation graph):
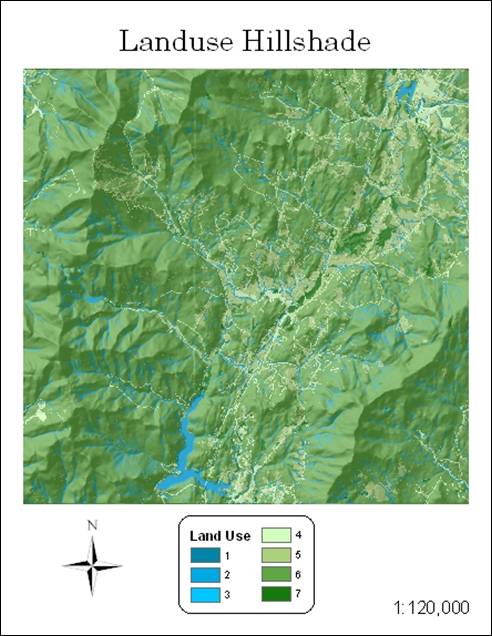
Hand-In 2 (hillshade):
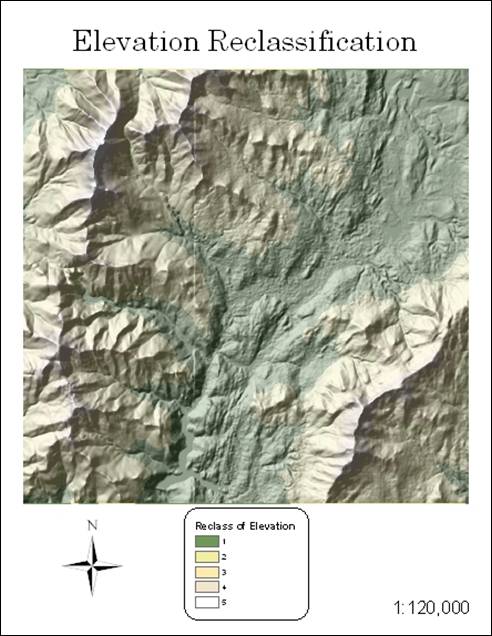
Hand-In 3 (elevation reclass with hillshade):
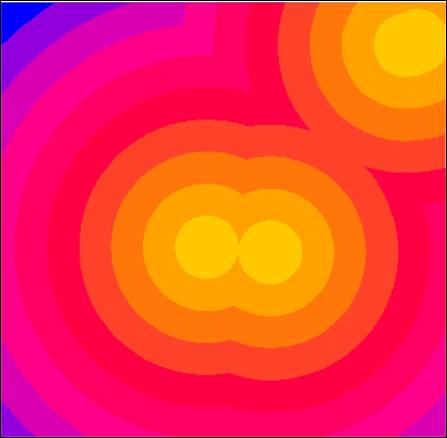
Hand-In 4 (distance to schools
grid):
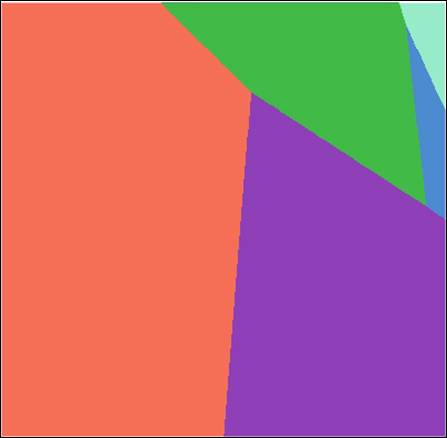
Hand-In 5 (allocation to schools
grid):

Hand-In 6 (raster calculation):
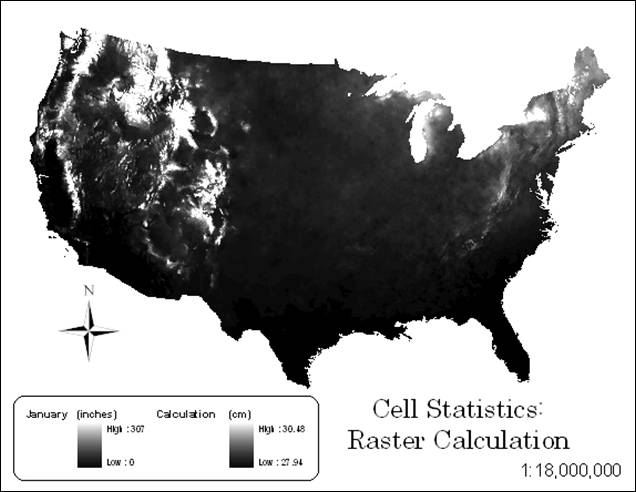
Hand-In 7 (relational operation):
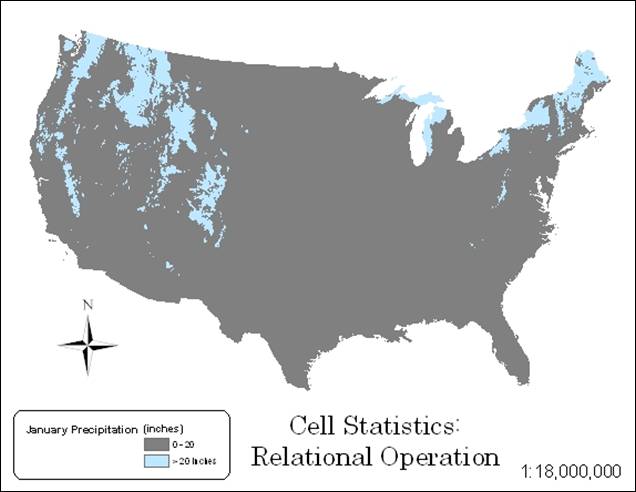
Hand-In 8 (raster addition):
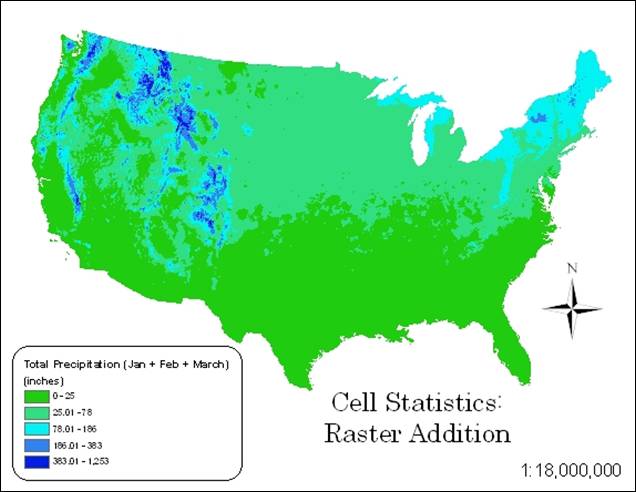
Hand-In 9 (neighborhood
statistics, range):
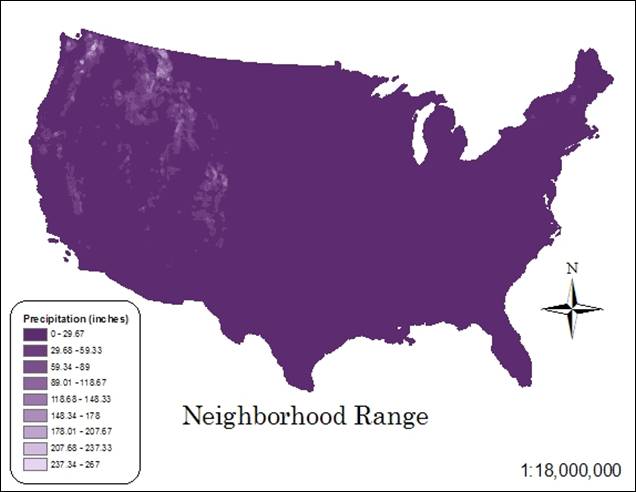
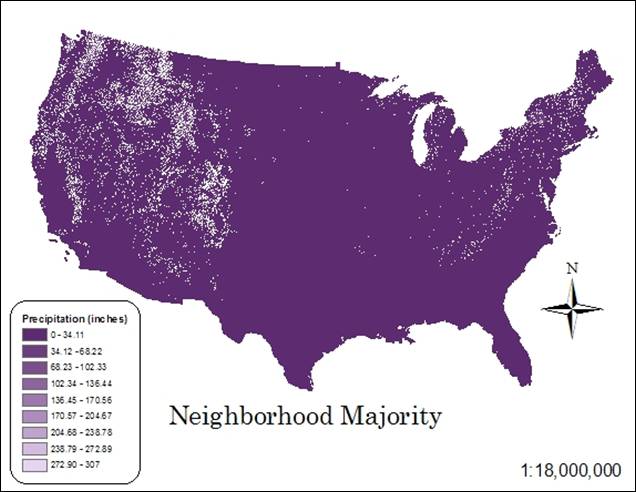
Hand-In 10 (neighborhood
statistics, majority):
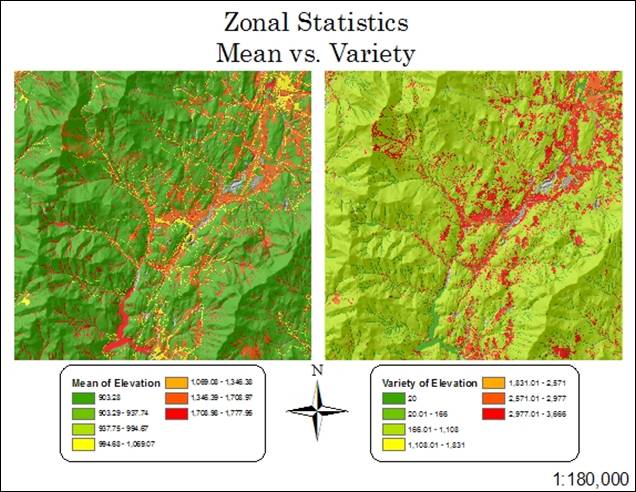
Hand-In 11 (zonal statistics, mean
vs. variety):
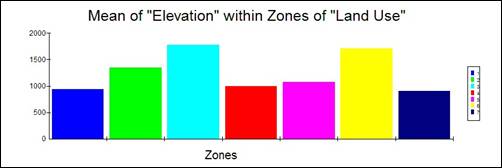
Hand-In 12 (zonal statistics,
graphs):
 нннн
нннн 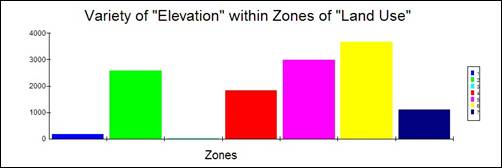
Hand-In 13 (boolean operations):
Hand-In 14 (mosaic):
Hand-In 15 (resample, size 200):
Hand-In 16 (resample, size 400):
Resample Supplement (200 resample
vs. 400 resample, graph):

Hand-In 17 (conversions):
Answer the following questions
1. While do we need reclassification sometimes? Give an example
where it is useful?
Reclassification is needed to group objects based on
certain conditions, or to assign new class values to the original class. Topographic or bathymetric
values can be reclassified to show only a certain range of elevation or depth
to isolate an area of study.
2. In conducting neighborhood statistics, what are the
statistics types that you can use? What
types of neighborhoods are available in ArcGIS? Can you give two examples where such
statistics and neighborhoods can be used?
Neighborhood statistics available
are minimum, maximum, range,
sum, mean, standard
deviation, variety, majority, minority and median. Neighborhoods can be annulus, circle,
rectangle or wedge. Examples might be a
dot map showing maximum harvested crop areas, or the average household income
in a census tract.
3. In conducting Zonal statistics, what are the major statistic
types are available? Give two examples
whether they could be useful?
The zonal
statistic types are minimum, maximum, range, sum, standard
deviation, variety, majority, minority and median Areas in need of irrigation could be
determined from zones of minimum rainfall and temperature value. Also, preferable skiing locations could be
mapped based on zones of maximum snowfall and elevation value.
4. Why do we need to do resampling sometimes?
Resampling is necessary when
overlaying rasters of different coordinate systems or
different cell sizes. This way the raster
layers are compatible, thus avoiding ambiguous overlay.